Redundant Connection
冗余的连接; LeetCode 684; LintCode 1088
In this problem, a tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles.
You are given a graph that started as a tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n, with one additional edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from 1 to n, and was not an edge that already existed. The graph is represented as an array edges of length n where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a tree of n nodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the input.
Example 1:
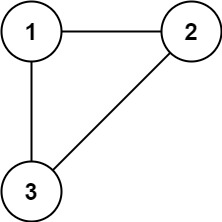
Input: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: [2,3]Example 2:
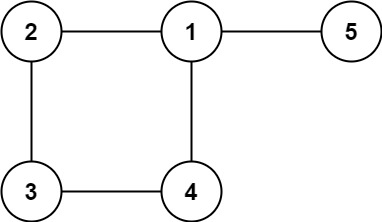
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]]
Output: [1,4]Constraints:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ai < bi <= edges.lengthai != biThere are no repeated edges.
The given graph is connected.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
这题有官方solution。思路是:
这个套路很巧妙,之前没有碰到过。大概就是说,如果u,v本来就是连通的(在加入这条edge之前),那么这条edge就是多余的。
根据这个思路,有dfs和union find两种做法。我的code在下面。然后后面还有我自己的第三种的做法
----------------------------
下面是我没看solution前写出来的做法。思路就是dfs来找环,找到环后,在这个环上找一条最后出现在edges中的边来作为答案
Last updated
Was this helpful?